- Protocol conversion between CAN and Ethernet interface
- Protocol conversion between CAN and serial port
- Train Control and Management System (TCMS)
- Train Communication Network (TCN)
- Embedded application and development
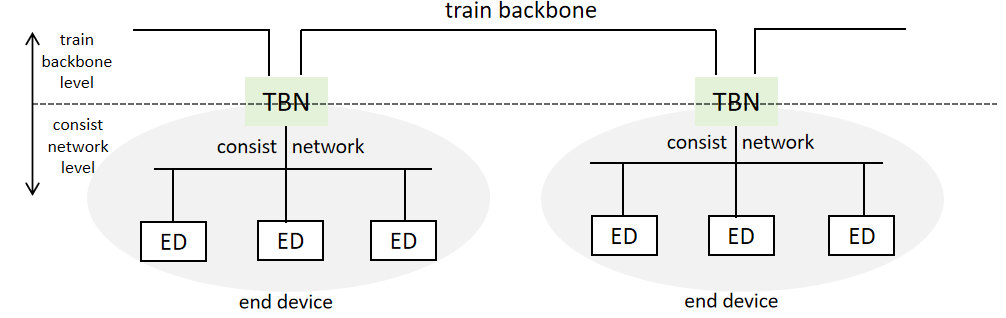
TCN has a two level network structure, namely Train Backbone and Consist network.
• Train Backbone
1)It may use WTB or ETB.
2)It may use both WTB and ETB simultaneously. (For example, use WTB for operational data and ETB for multimedia data, and connect WTB and ETB with a Gateway.)
3)It may use multiple ETBs simultaneously. (A maximum of 4 ETBs.)
4)For a statically - configured train, there may be no Train Backbone.
• Consist network
1)It may use MVB, CAN, or ECN.
2)There may also be no consist network, and end devices are directly connected to the backbone network nodes.
WTB(Wire Train Bus)
A serial data communication bus mainly designed for open train interconnection, with the corresponding standard being IEC 61375-2-1.
ETB(Ethernet Train Backbone)
The Ethernet Train Backbone Network realizes an open train data communication system based on Ethernet technology, and the corresponding standard is IEC 61375-2-5.
MVB(Multifunction Vehicle Bus)
Multifunction Vehicle Bus, which is used to connect the devices in the Consist network, and the corresponding standard is IEC 61375-3-1.
ECN(Ethernet Consist Network)
The Consist Network based on Ethernet technology corresponds to the standard IEC 61375-3-4.
RTP(Real-Time protocols)
In the TCN architecture, the WTB and MVB buses use the same RTP protocol (described in IEC 61375-2-1), and mainly provide two types of communication services for applications:
• Variables: Transmit short data with deterministic delay. (e.g., Process Data PD)
• Messages: Transmit data that may be very long but is transmitted infrequently. (e.g., Message Data MD)
TRDP(Train Real-Time Data Protocol)
In the TCN architecture, the ETB and ECN networks use the TRDP protocol (described in IEC 61375-2-3) to exchange Process Data (PD) and Message Data (MD):
• Process Data (PD): PD data is sent periodically or upon request between the publisher and the subscriber.
• Message Data (MD): MD data is sent upon request between the caller and the replier.

